B99 Biodiesel as a Heavy Duty Fuel
Using B99 Biodiesel in a Tier 4 Heavy Duty Diesel
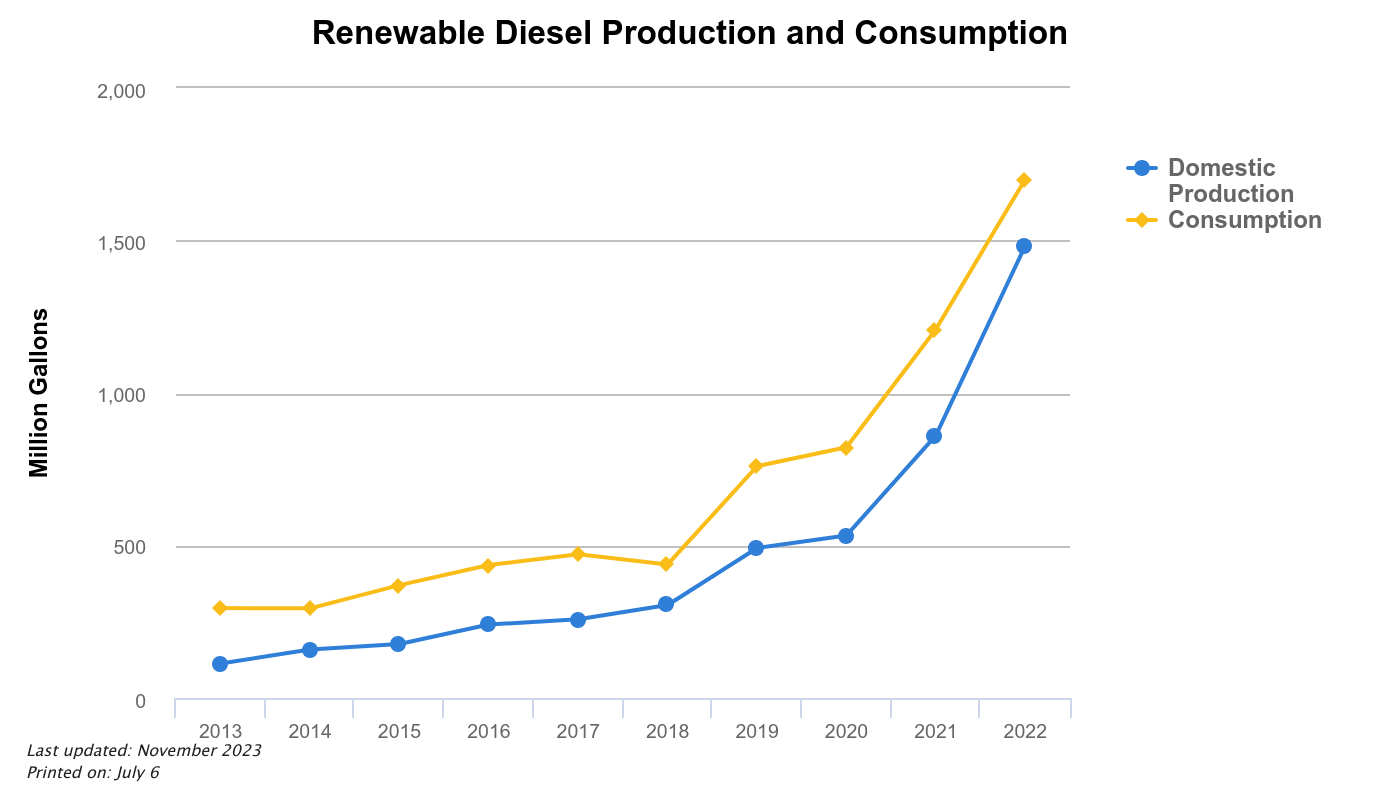
B99 Biodiesel reduces CO2 footprint of a 105,500 GVW truck and trailer by more than half at a lower cost than petroleum diesel.
What is B99 Biodiesel?
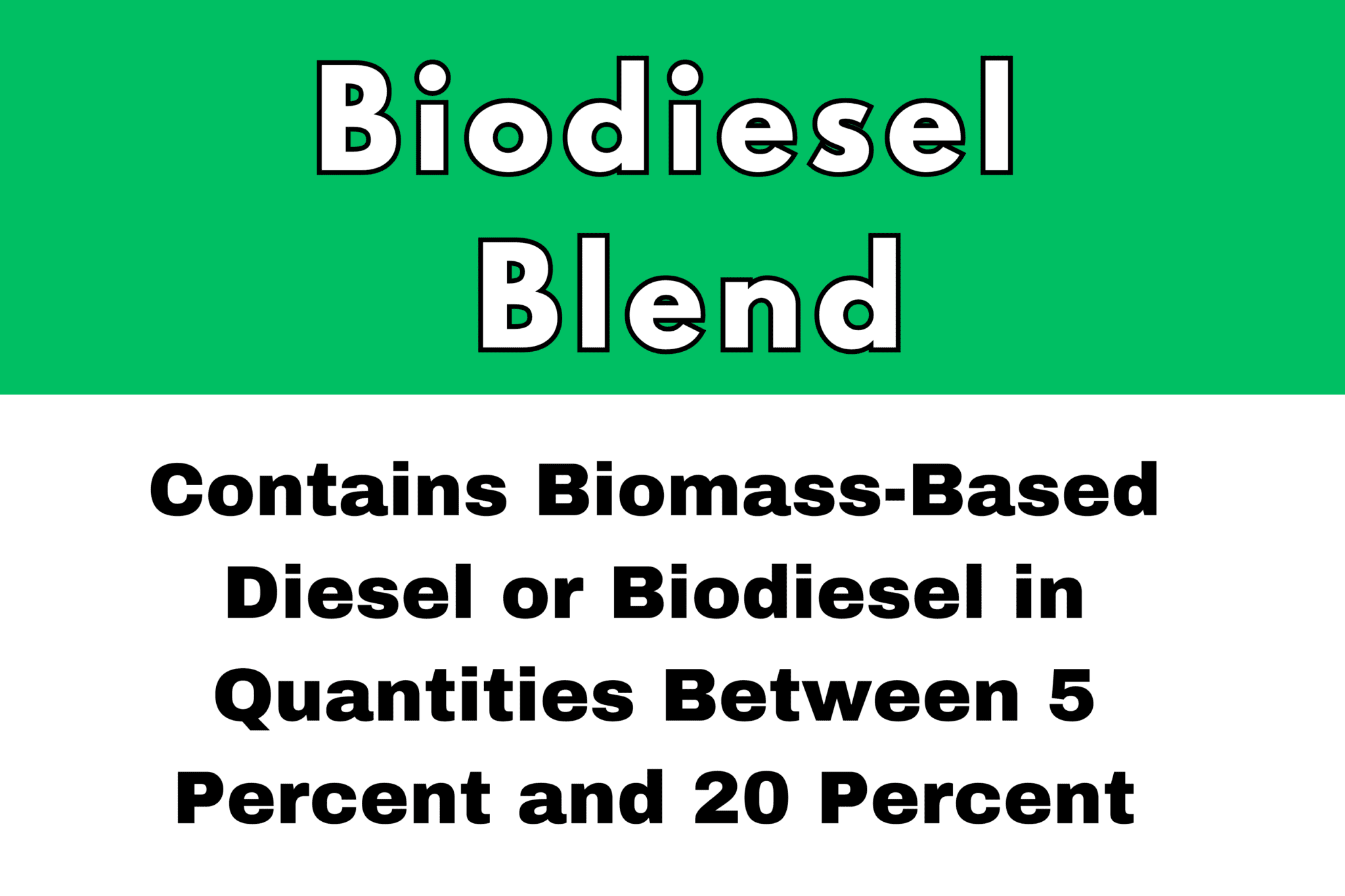
B99 Biodiesel is as pure of blend of Biodiesel you can get in the United States and still participate in the incentives associated with this alternative fuel. B99 is the product received by petroleum refiners, terminals, and truck stops to blend with petroleum diesel. Biodiesel is a renewable, clean-burning diesel replacement. B99 Biodiesel is a common blendstock with petroleum diesel (being 99% biodiesel). It can be presumed that nearly every major truck stop throughout the US is consistently using either a blend of 5%, 10% or 20% of biodiesel The reason for this is both due to its price advantage against petroleum currently as well as Federal/State laws requiring it’s use.
Why Higher Blends of Biodiesel Matter?
Biodiesel is a low CO2, net energy positive fuel. Depending on the feedstock Biodiesel is made from a CO2 reduction of 30% to 80%+ can be expected compared to petroleum diesel. As the West Coast (Oregon, Washington and California) ramps up CO2 regulations that charge an additional cost for carbon emissions associated with petroleum diesel the financial case for Biodiesel becomes obvious. Early adopters will see direct financial benefit.
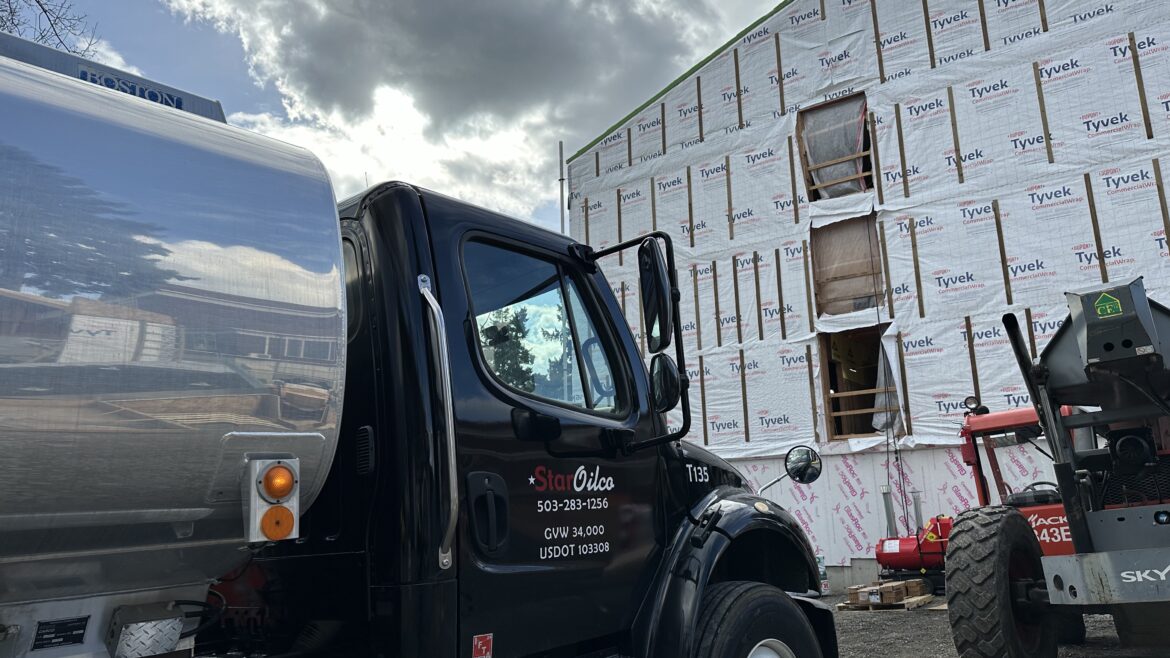
Star Oilco has fielded the Optimus Technologies system on our 105,500 GVW truck and trailers. Star Oilco began with a single Freighliner truck and trailer operating a Cummins ISX as a trial. This truck’s typical route was approximately 305 miles round trip from Portland, Oregon to Grays Harbor, Washington. This run is from Star Oilco in Portland, Oregon to the Grays Harbor REG Biodiesel plant and back to the Portland terminals for delivery of this product. Over the last year and a half this truck has performed amazingly well, the only maintenance concern is swapping the fuel filters more regularly with every oil change. Mileage and power difference are negligible as noticed by drivers or our Elog system. On a few occasions a loss of power was experienced requiring an in between service fuel filter swap.
This field trial of the Optimus Technologies system Star Oilco has regularly saved between $15 and $75 a day when running this dedicated route, depending on the cost of B99 Biodiesel versus petroleum ultra low sulfur diesel. Consistently the price of B99 Biodiesel has been below petroleum diesel in the Portland, Oregon market. This has been due to a combination (or is effected by) RIN values, a Blender’s Tax Credit on biodiesel, and Oregon’s Clean Fuels Program which also prices the CO2 reduction value of B99 Biodiesel. We see this trend continuing as an assumed market reality for biodiesel.
What is the business case for our deploying B99 Biodiesel Optimus Tech upfit kits?
The systems increase the intelligence of our late model trucks with their very complicated Tier 3 and Tier 4 emissions systems. The Optimus Kit enables two saddle tanks to operate with the duty cycle of the truck. One tank (which we will be running B5 ULSD or R99 through) is dedicated to fuel the particulate trap and SCR systems. These systems have extremely tight tolerances and tend to choke on higher blends of biodiesel. By dedicating a tank with a smart controlling system we reduce the maintenance and concern with these after treatment systems hopefully extending the maintenance cycle on these traps by years while reducing inconvenient efficiency killing regens.
The Optimus Kit also enables a modern diesel engine to run B99 Biodiesel. It does this by controlling the temperature of the fuel in it’s dedicated saddle tank and routing B99 to the engine when the RPMs and operating temperatures are best for this fuel. Upon start up and shut down the Optimus Technology kit will flush the engine, fuel rail, and injectors with the petroleum/R99 tank ensuring easy start up and no cold weather effects. The B99 saddle tank is temperature controlled as well to enable performance in extreme weather. When operating under load the Optimus Kit will move to B99 as the fuel into the engine. As B99 Biodiesel has a substantial reduction of emissions, particulate, and other compounds when combusted; this further reduces the impact of miles on a truck to the particulate trap and it’s service needs.
Beyond this maintenance experience, the performance and function of the system has been indistinguishable to our other trucks running the same route.
Biodiesel Mandates in the Pacific Northwest
Oregon and Washington have passed legislation which puts a price on the CO2 emissions associated with petroleum diesel. These laws mean that petroleum fuel costs more than biofuels with a low CO2 footprint. These laws are also added on top of other mandates and incentives for biofuels. Biodiesel blends between 5% and 20% are common on the west coast at every gas station, cardlock, and truckstop.
How Can I Utilize B99 or B100 in My Own Fleet?
Star Oilco uses The Vector System developed by Pittsburgh-based Optimus Technologies. The Vector System is the only EPA-compliant biodiesel engine system and upgrades any medium or heavy-duty engine to operate on 100% biodiesel. It can be installed in as little as 12 hours. Learn more about The Vector System by contacting Optimus Technologies here directly or by reaching out to Star Oilco locally.
Contact Form
For more on Biodiesel, Renewable Diesel or Low CO2 fuels please see these other Star Oilco articles:
Every Question Star Oilco has been asked about Biodiesel
Every Question Star Oilco has been asked about Renewable Diesel
Do you have questions about Renewable Diesel in Oregon