Oregon Self Serve Gasoline
Oregon Governor Tina Kotek signs historic Consumer Choice (Self Serve) Gasoline bill.

Self Serve Gasoline law awaits Governor’s Signature.
Oregon Self Serve Gasoline FAQs:
Q: Can I self serve gasoline at a cardlock location?
A: Not unless you are doing so for a commercial use.
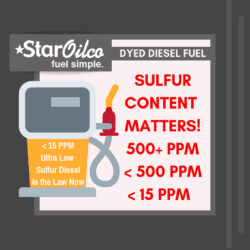
The Gas Self Serve bill requires for retailers to provide Full Serve as an option alongside Self Serve gasoline. Diesel fuel can be self served and the general public can fuel themselves with diesel at a Commercial Cardlock now. For gasoline customers, as cardlock does not offer full serve we can not open it up to the general public. Commercial Cardlock is regulated by the Oregon State Fire Marshall who still requires a business purpose for self serving gasoline at a 24-7 stand alone cardlock.
Q: When does Self Serve become available at a retail gas station?
A: Friday August 5th, 2023 is when consumers can opt to fuel their own gasoline in Oregon.
Q: What if I do not want to self serve my own gasoline?
A: The new Self Serve gasoline rules in Oregon require that any retail gas station offering self serve also provide full serve.
There must be well marked islands for Self Serve Gasoline and Full Serve gasoline service. Anyone wanting full service will still have it as an option. The law also requires that all sites have no more Self Serve fueling pumps as Full Serve fueling positions. So Full Service gasoline will be readily available at any site offering Self Serve gasoline. The law also expressly requires that there is no difference in price between Full Serve and Self Serve gasoline.
Oregon Self Serve is Legal in Oregon State
Oregon Self Serve at retail gas stations is coming to consumers who want it. The Oregon Legislature has passed HB2426, a law that would give consumers a choice if they want to serve their own gasoline at a retail gas station. This law is awaiting the Governor’s signature to be signed into law.
As the Legislature has adjourned, Governor Tina Kotek has 30 days from when the Bill was passed to sign it into law, veto it, or let it expire without signature.
THE HISTORY OF FULL SERVE LEGAL REQUIREMENTS IN OREGON
Oregon outlawed self serve gasoline in 1951. The trend for self serve as a business model started in California. The first self serve retail gas station was in 1947 in Los Angeles. The restriction on serving your own gasoline had a basis in public safety and was not allowed by the Fire Codes in most states. With the potential for large self serve gas stations coming Oregon made a decision to prevent the widespread adoption on a fire safety basis.
Inside the Oregon fuel industry there are anecdotal stories of the full serve mandate law coming from a coalition of consumers and local fuel sellers resisting bigger entrants to the market with huge numbers of fuel islands and few employees. Full service gas was viewed as a competitive advantage for local gas stations that was also preferred by consumers. In the 1980’s a few attempts were made to legalize self serve in Oregon and was resoundingly shot down by the public. The growth of Oregon’s cardlock industry came out of this as business allowances were made for self serve gasoline with 24-7-365 access to fuel.
HB2426: SELF SERVE IS A CHOICE, NOT A REQUIREMENT
Talk to any longtime born and raised Oregonian, Full Serve Gas is a cherished right of Oregon residency. This right will not be extinguished with this law. Self Serve in the more populated parts of Oregon will require Full Serve as a choice. The point of this law is to get wider service available for gas stations currently forced to close, operate at reduced island capacity, or reduced hours due to labor shortages.
BACKGROUND ON GASOLINE RETAIL IN OREGON:
Oregon has required gasoline be served by an attendant at retail gas stations. Gasoline is a Class 1 Flammable Liquid. Under a safety basis this fuel was restricted to only professionals and businesses to dispense it. Diesel, which is a Class 3 Flammable Liquid because it catches fire at a higher temperature was not restricted from self serve.
In 2015 the more rural and less populated counties of Oregon were allowed to use self serve gasoline as a strategy to increase service hours at gas stations. In 2017 this policy was expanded to more rural counties in Oregon. The rules required options for full service gas service during predictable hours for those wanting or needing service. During the COVID lock downs due to extreme labor shortages as well as fear of human contact self serve was allowed statewide. With this House Bill 2426 all of Oregon can choose to serve gasoline themselves if they want.
HB2326 – THE OREGON SELF SERVE LAW:
HB 2326, as a statute, has a great deal of legal detail. We have paraphrased and simplified the language of HB2326 as it relates to the self serve subject below:
A gas station selling gasoline at retail may not designate more than the same number
of fuel pumps for self-service as are available for full service.
Retail gas stations must:
Post signage clearly showing what fuel pumps are self serve and which are full service.
Designate at least one person to be available to pump fuel for those needing full service.
In the more populous counties of Oregon, any gas station must provide a Full Service attendant during any hours they offer the choice of self serve gasoline.
Gas stations opting to allow self serve fuel pumps cannot charge a different price for Full Service or Self Service gasoline at those pumps.
If you have any questions about Oregon’s Self Serve legal change please feel free to reach out to Star Oilco. If we do not have the answer to your questions we will find it for you.

























 Star Oilco is an Independent Franchisee of Pacific Pride
Star Oilco is an Independent Franchisee of Pacific Pride






















