B20 Biodiesel, a Proven Fuel
Using Biodiesel in the Pacific Northwest.
(NOTE: B20 refers to 20% biodiesel blended with an 80% petroleum diesel percentage. B5 refers to 5% biodiesel blended with petroleum diesel which is the legally required blend percentage in Oregon state. For more on biodiesel basics, visit the US DOE.)

Biodiesel is the “Drop In Solution” used in the Pacific Northwest to reduce CO2 emissions in diesel equipment.
If you are looking to use Biodiesel in a fleet or a personal vehicle it is as easy as just asking for it. In Oregon the fuel is everywhere. From an Oregon and Washington state requirement for a minimum 5% of biodiesel blended with every gallon to large financial incentives this low carbon diesel fuel is ready for you if you want it.
It’s not just the Pacific Northwest. For years B20 has been a defacto blend at some of the biggest names in fuel. When you pull up to the pump on the west coast you are likely getting B5 or B20 as a blend. In Oregon, B5 biodiesel is the required fuel by law. Oregon also has a B20 incentive for a waiver of state on road taxes. Washington as well has requirements that biodiesel finds its way into retail and commercial diesel throughout the state. Additionally, Oregon and California have “Clean Fuel Standard” programs which heavily incentivize low CO2 fuels like biodiesel. Washington state is expected to pass their own Clean Fuel Standard as well this year. Biodiesel has been a fact of life in fuel for over a decade in the United States and Pacific NW and it is not going away.
Due to a mix of federal and state incentives to use biodiesel, there can also be financial advantages for a fleet dedicated to making B20 biodiesel its fuel of choice. You can see evidence of this at truck stops and other retailers making B20 available in Oregon and Washington, as well as in the trucking lanes of the United States. America’s largest fleets are choosing B20 biodiesel in order to reduce their cost per mile. So can you.
In an effort to deliver the best value to truckers, many U.S. truck stops are blending biodiesel up to 20% when the market enables them to pass along a lower cost yet high quality ASTM specified diesel fuel to their customers. Most prominent is Pilot/Flying J, who lists where and when their sites are serving up B20 or lower blends. Pilot/Flying J buys biodiesel directly and blends on site in order to give their customers the best value possible. Loves Travel Centers also sell biodiesel blends around the U.S.
In Oregon, due to a diesel road tax waiver on B20 sales, gas station retailers Safeway, Leathers Fuel, Spaceage, and others are offering B20 biodiesel as their retail diesel offering. Oregon’s system requires the biodiesel be sourced from used vegetable oil refined biodiesel products. Biodiesel has been in Oregon’s fuel supply since 2006 when the city of Portland mandated B5 biodiesel blends within its city limits. The state of Oregon followed Portland with its own statewide mandate not long after.
(NOTE: If you operate a retail gas station and are curious about Oregon’s fuel tax breaks for biodiesel blends here is a more in depth article Oregon Biodiesel Tax Breaks for Retail Fuel Stations that explains these rules for retailers of fuel).
Biodiesel has been in our fuel system since 2006 and the technology that goes into making it has vastly improved. It is proven in diesel engine performance while also creating a diversified supply for energy and significantly reducing emissions from the working fleets of the world. Biodiesel substantially reduces emission coming out of your stack without a major impact on price because it helps to offset high diesel prices.

If you want to look at using B20 blends in your fleet, we are here to help. Star Oilco carries B20 blends for mobile onsite refueling every day of the week. We also have dyed/off-road/heating oil blends of B20. If you are an over the road fleet we can provide B20 at our cardlocks as well as help you procure it with a fleetcard over the road. Let us know if we can be of help.








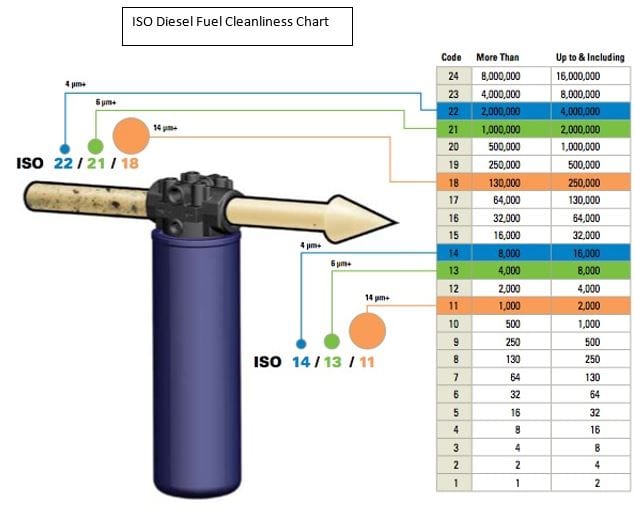
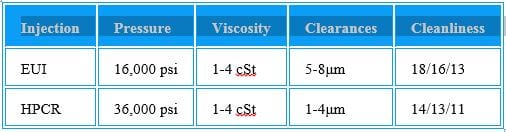
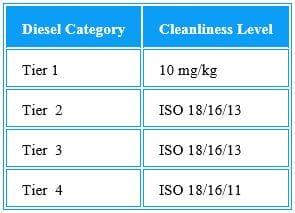
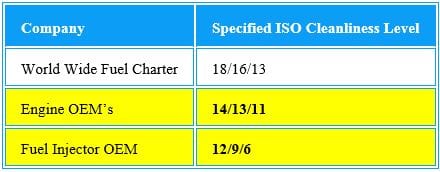






 Oregon law has a 5% Biodiesel and 10% Ethanol fuel blend mandate.
Oregon law has a 5% Biodiesel and 10% Ethanol fuel blend mandate.




