What Is The Renewable Fuel Standard In Portland?
Did you hear about the time Portland banned fossil fuel diesel?
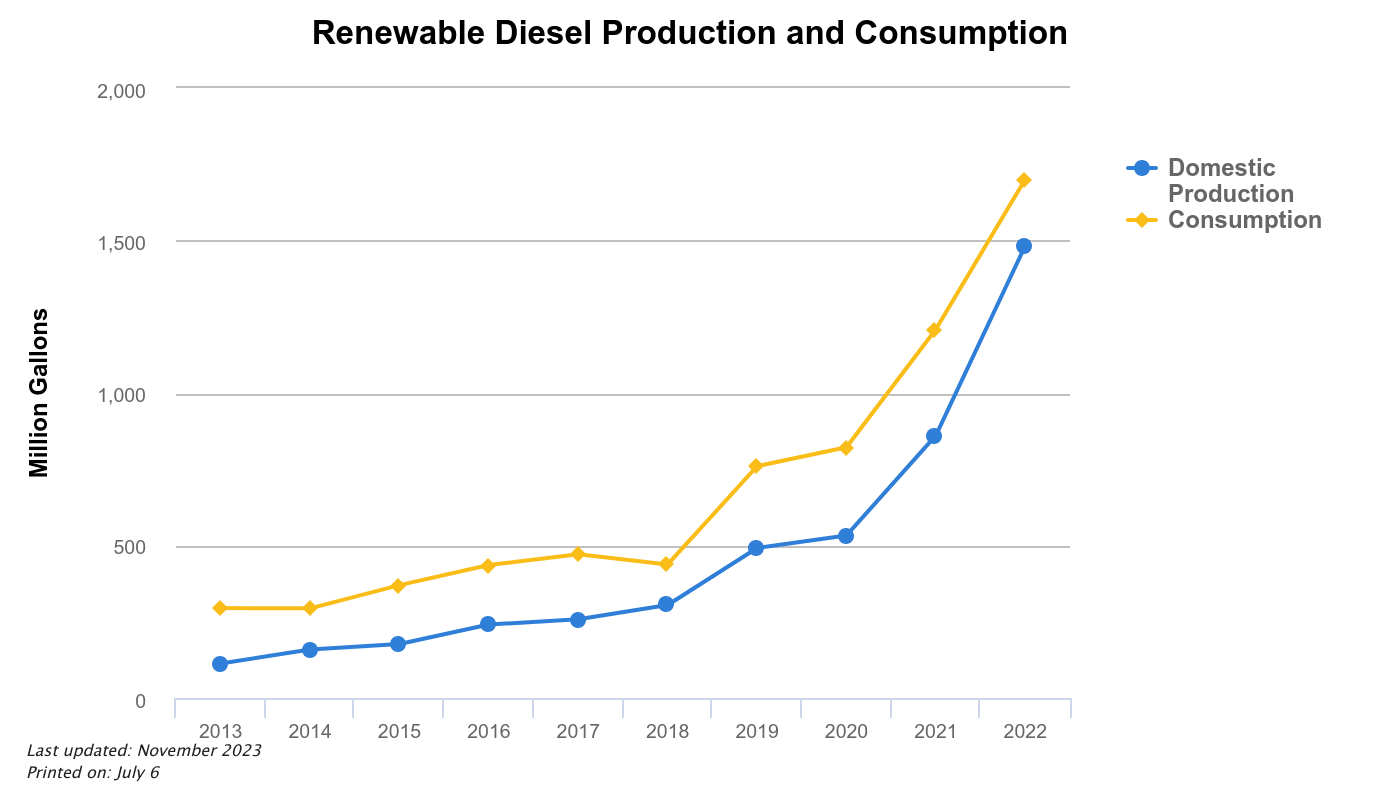
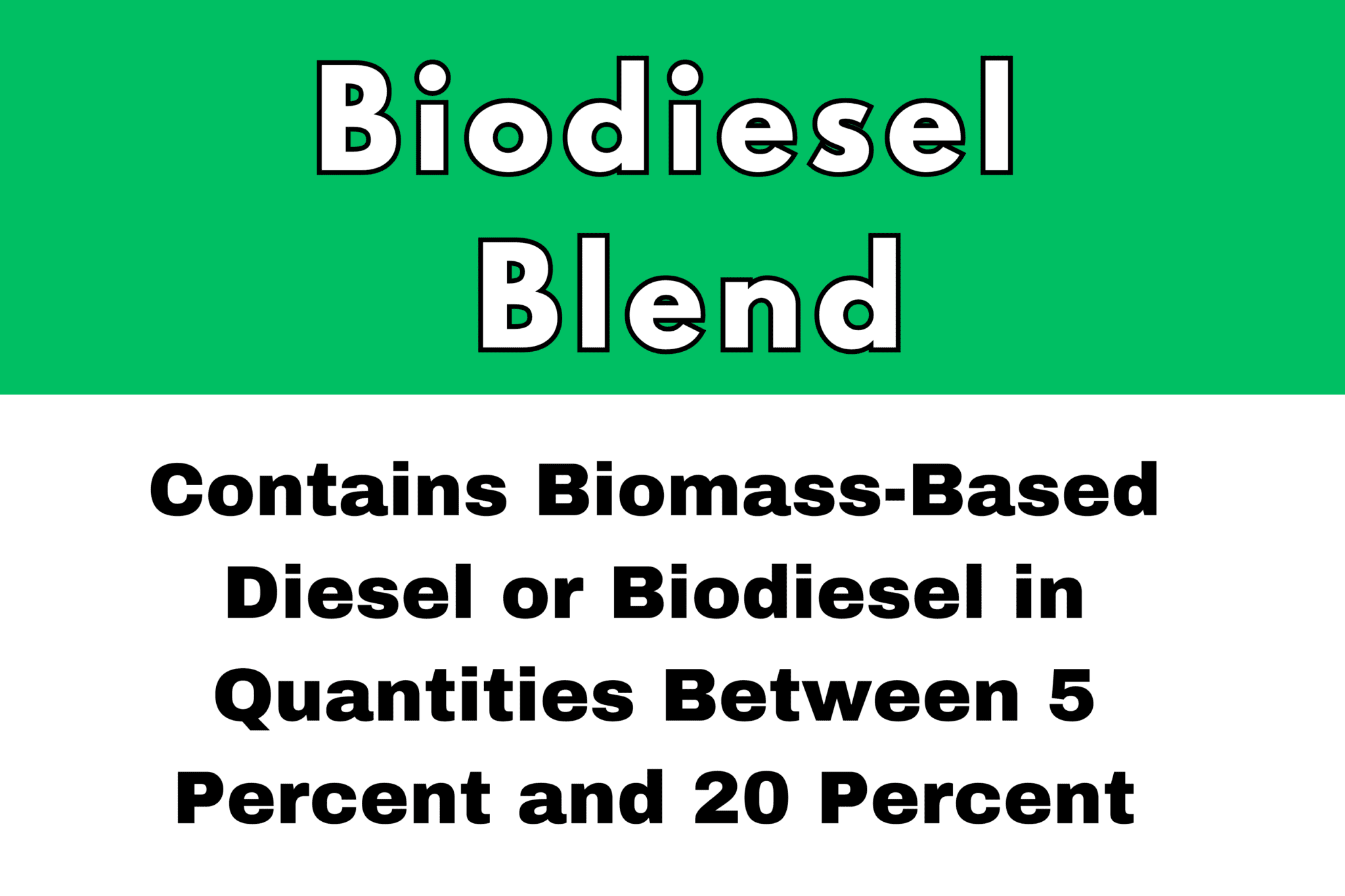
Portland is making a big move to provide cleaner air and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Portland has implemented what’s called the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) beginning its first phase on May 15th, 2024. The RFS policy in Portland mandates that there has to be an increase of use of low-carbon biofuels in diesel within city limits of Portland. This is part of the ultimate Climate Emergency plan. This RFS mandate was first implemented in 2006 as a B5 (5%) Biodiesel blend mandate with the goal of mandating a 20% blend. The RFS is the first of its kind not only in Oregon but in the entire United States. Portland’s reputation as a leader in environmental sustainability efforts continues.
Portland’s Phases To Implement Almost 100% Renewable Diesel
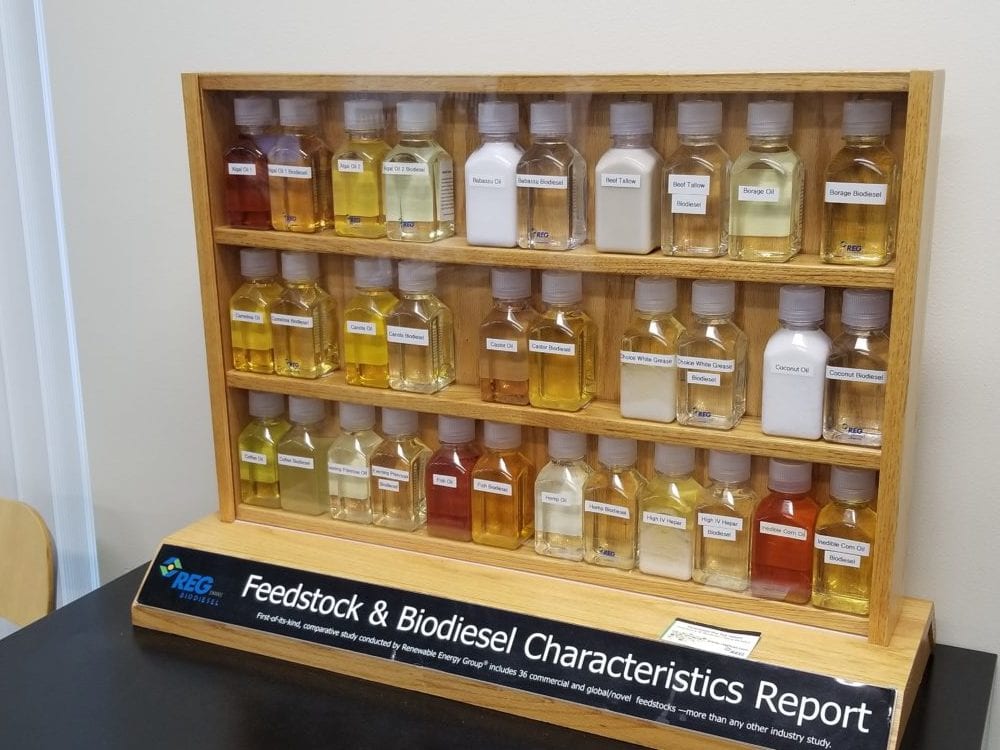
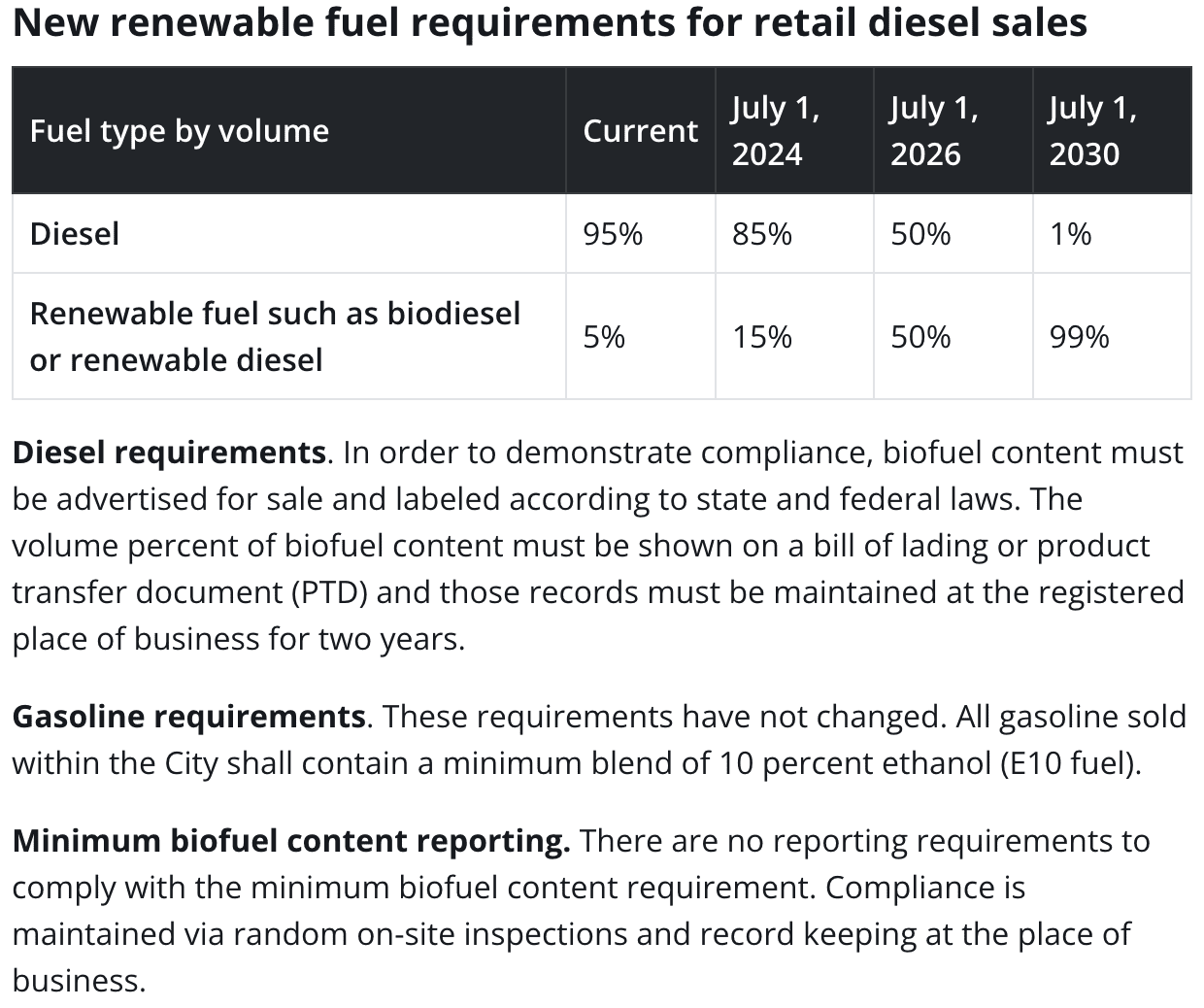
What makes Portland’s mandate unique is the requirement that the biofuels have a CO2 value so low it bars most American made biodiesels. The blending requirement starts at 15% in 2024, and then it will steadily increase to 50% by 2026 and will reach 99% by 2030. This schedule demonstrates how Portland’s low-carbon ambition is present to transition away from fossil fuels and promote alternative energy sources.
This policy is expected to reduce air pollution and carbon emissions. It will also create new markets for biofuels, which will lead to increased economic opportunities. This will ultimately help the city become a more sustainable and environmentally friendly place to live as Portland has taken the lead in striving for sustainability over the years.
The policy will also help create jobs in the biofuel industry and provide opportunities for businesses to switch to renewable energy sources. It will also help reduce the city’s dependence on fossil fuels and protect the environment for future generations.
Want to learn more about meeting Portland’s requirements for the Renewable Fuel Standard mandate?

Focus on Lower-Emission Biofuels
Uniquely, Portland’s RFS goes beyond just the biofuel blend. It also sets a strict carbon intensity (CI) standard for the biofuels themselves. This ensures the biodiesels used have a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to traditional options. Biodiesels produced domestically often fall short of this CI requirement, prompting many suppliers to look to renewable diesel sources. This focus on biofuels with a lower lifecycle carbon footprint makes Portland’s RFS even more impactful in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.

Exemptions and Implementation Details
The initial phase of the RFS targets on-road diesel sales. This applies to diesel purchased at gas stations, by mobile fueling companies, and for use in large stationary tanks. However, the long-term goal includes all diesel use within the city. Some temporary exemptions apply to off-road diesel uses such as heating oil, generator fuel, aircraft fuels, watercraft fuels, and other dyed fuel users. One local truck stop, Jubitz Truckstop, was granted a temporary exemption. This is likely due to concerns about disrupting critical transportation operations. Daimler (the manufacturer of Freightliner and Western Star trucks) has a research facility in Portland. Daimler was also granted an exemption to meet their specific fuel needs for testing purposes.
The RFS enforces compliance through fuel sampling and requires documentation proving the fuel meets the minimum biofuel content and CI standards. Businesses that purchase diesel need to be able to show their compliance through bills of lading (BOLs) or similar records from their fuel provider, like Star Oilco. If a business does not comply and provide this documentation, it can result in pretty hefty fines. First offenses can be a fine of $10,000 per day. Repeat offenders will end up facing even bigger penalties of up to $15,000 per day. These fines can really show the impact of how serious Portland is taking this initiative.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
While residential consumers who don’t purchase diesel directly are not directly impacted, businesses purchasing diesel, especially in bulk, will need to adapt to the new regulations. This may involve acquiring documentation from fuel suppliers or entering into contracts guaranteeing compliant fuel blends. Wholesale fuel distributors, who sometimes purchase from multiple vendors and blend fuel mid-route, may face additional challenges in tracking the biofuel content and CI of their product. However, as the program matures, the industry is expected to adapt and streamline these compliance procedures.
A Step Forward for Cleaner Transportation
Portland’s ambitious RFS sets a new expectation for sustainable transportation. Promoting low-carbon biofuels allows Portland to aim to significantly reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and be able to contribute to cleaner air for its residents. The RFS program will be able to serve as a model for other cities that are looking at implementing similar initiatives. Great job Portland for paving the way to a sustainable future for other cities! Although challenges will remain, as businesses adapt to this new norm, Portland’s RFS represents a significant step forward in creating a more sustainable transportation sector.
The RFS program is an important step in the fight towards sustainability and lower carbon fuels. It sends a clear message that cities are willing to take action to reduce emissions and protect the environment. We anticipate that other cities will follow Portland’s lead and create similar initiatives. This will have a significant impact in reducing emissions and helping to protect the environment.
It is a positive step towards a more sustainable future. Alternative fuels have become more and more readily available. Investing in alternative fuels and reducing carbon emissions is essential for protecting the planet for future generations. Governments should prioritize investing in renewable energy sources and incentivize communities to switch to alternative fuel solutions.
Thank you for choosing Star Oilco as your preferred fuel provider in Portland and Vancouver, Washington. Give us a call to discuss how the RFS mandate can affect your business and one of our team members would be happy to discuss this with you.
























 Star Oilco can provide your project with the fuel you request.
Star Oilco can provide your project with the fuel you request.