The Future of Diesel Fuel

Diesel Fuel In Oregon and Washington
Star Oilco has been getting questions on the changes of diesel in Portland, Oregon. If you have not noticed, many diesel pumps at retail gas stations and cardlock have seen changing stickers on the face of the fuel pumps. As of July 1st, 2024 the City of Portland requires a minimum 15% biofuel content of all diesel sold. This policy is called the Portland Renewable Fuel Standard.
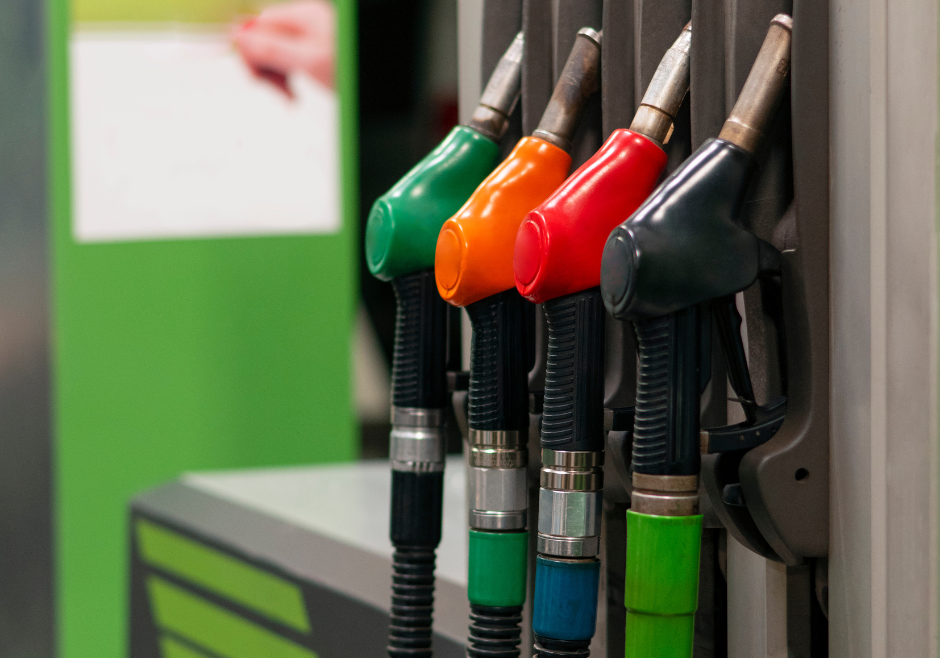
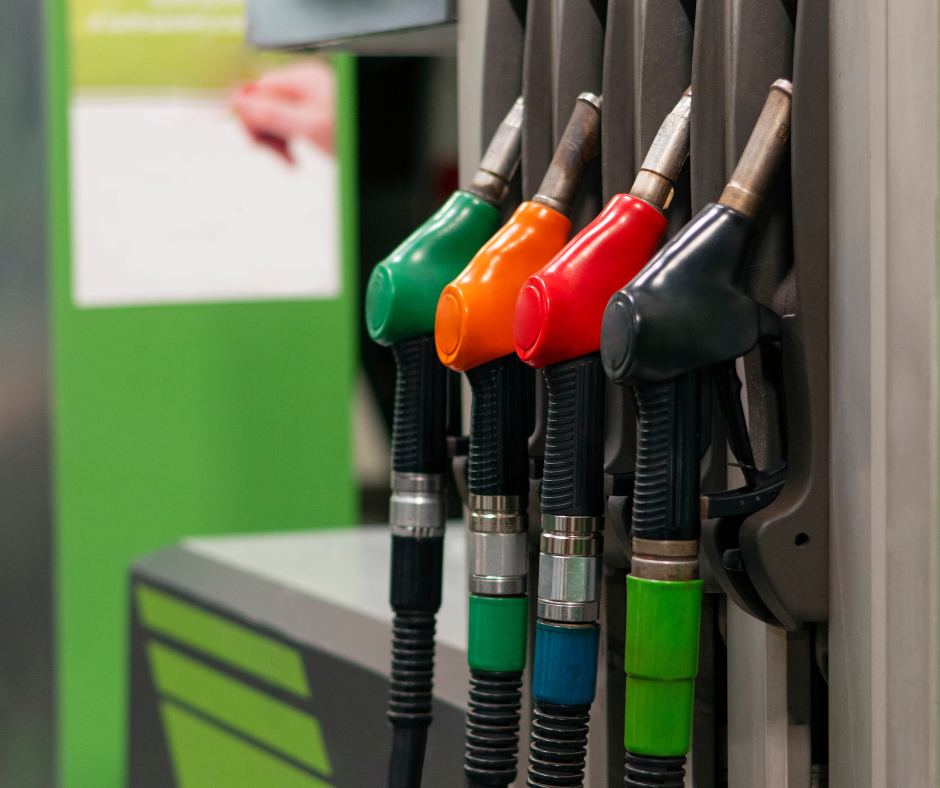
This has caused quite a few changes in what fuel pumps have for fuel. Diesel fuel buyers are noticing the bright yellow color of B20 biodiesel, the water clear color of Renewable Diesel or a a mix of several fuels tinting the color of their diesel. This trend is bigger than just Portland.
Today on the west coast there are a variety of product label stickers you will see on diesel pumps. These show the variety of diesel fuel specifications that are being sold to diesel vehicles today. Blends of petroleum ultra low sulfur diesel, R99 (99%) renewable diesel, and B99 (99%) Biodiesel are combined to meet the market needs of the diesel we all buy.
This change is because of a combination of pure market forces, government rules and local decisions by fuel haulers. Today’s diesel not only has a commodity market for the fuel it also has a market for CO2 credit value and a cap of total petroleum diesel fuel that can be sold into a west coast state with a “Cap and Invest” program requiring blends of low CO2 biofuels, the liquid fuels sold for vehicles.
Add on top of these market forces, advances in technology used to make the liquid diesel fuel. The diesel arriving at truck stops, gas stations, cardlock or out of a hose from a bulk truck has been changing and it’s often in good ways. Knowing how can be helpful in navigating why diesel may cost one price or another and may have a need or maintenance that another fuel does not.
THE RISE OF RENEWABLE DIESEL
Renewable diesel is a synthetic diesel fuel made from the same feedstock as biodiesel, but the finished product is hydrocarbon diesel. Though it is a biofuel, it is also diesel. For fuel regulation they refer to it (as well as biodiesel) as “Biomass Based Diesel” for labeling at the fuel pump.
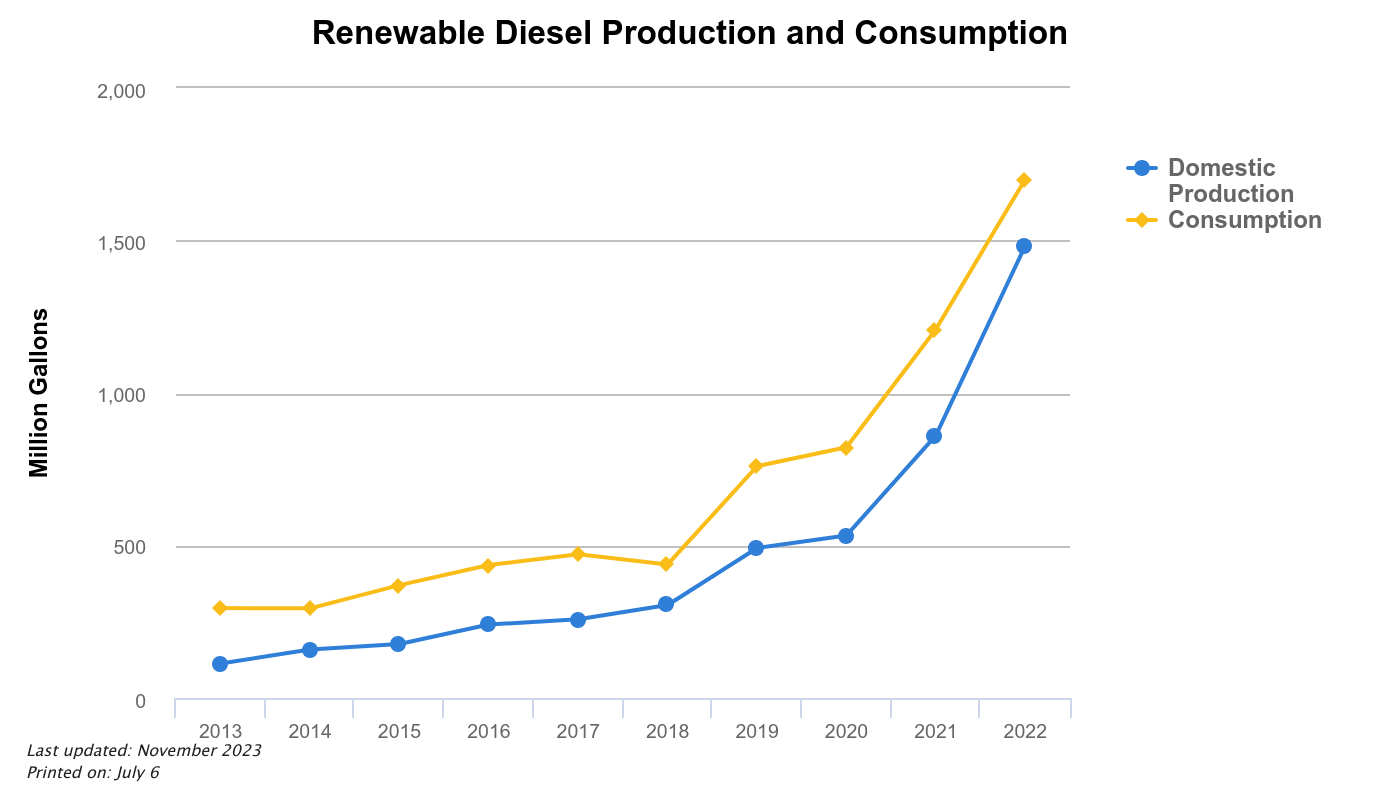
There have been billions of plant capacity brought online for renewable diesel. During the COVID collapse of fuel prices a number of petroleum refineries shut down, then upgraded their technology to make hydrocarbon diesel fuels out of the very biobased fats, oils, and greases biodiesel is made from. These refineries use hydrotreating technology just like they do with a crude petroleum to make an actual hydrocarbon diesel molecule. With this technology adoption to make diesel and jet fuels from vegetable oils and animal fats billions of gallons of low CO2 diesel fuels are coming on the market and governments are requiring it’s use, such as Portland’s Renewable Fuel Standard.
THE AVAILABILITY OF BIODIESEL
The US makes billions of gallons of biodiesel. A fuel that’s quality and performance continues to improve. If you are not a fan of biodiesel in your fuel thinking strategically about the fuel will likely benefit your fleet operation. The big concern with diesel fuel in a ultra low sulfur world is water and dirt suspended in the fuel affecting the performance of diesel emission systems. With clean and drier quality specifications of B99 blend stocks today versus a decade ago the use of this fuel has grown substantially especially in the truck stop market.
When crude petroleum prices are high and therefore refined diesel prices are equally as high biodiesel is often an extremely competitive fuel. If a large seller of diesel (including petroleum refiners) can pick up pennies per gallons on millions of gallons sold they will do so. Therefore Biodiesel is often seen in diesel in small blends even if you do not see a label on retail pump. For blends above 5% a label is required for retail fuel sales. RTHWEST?


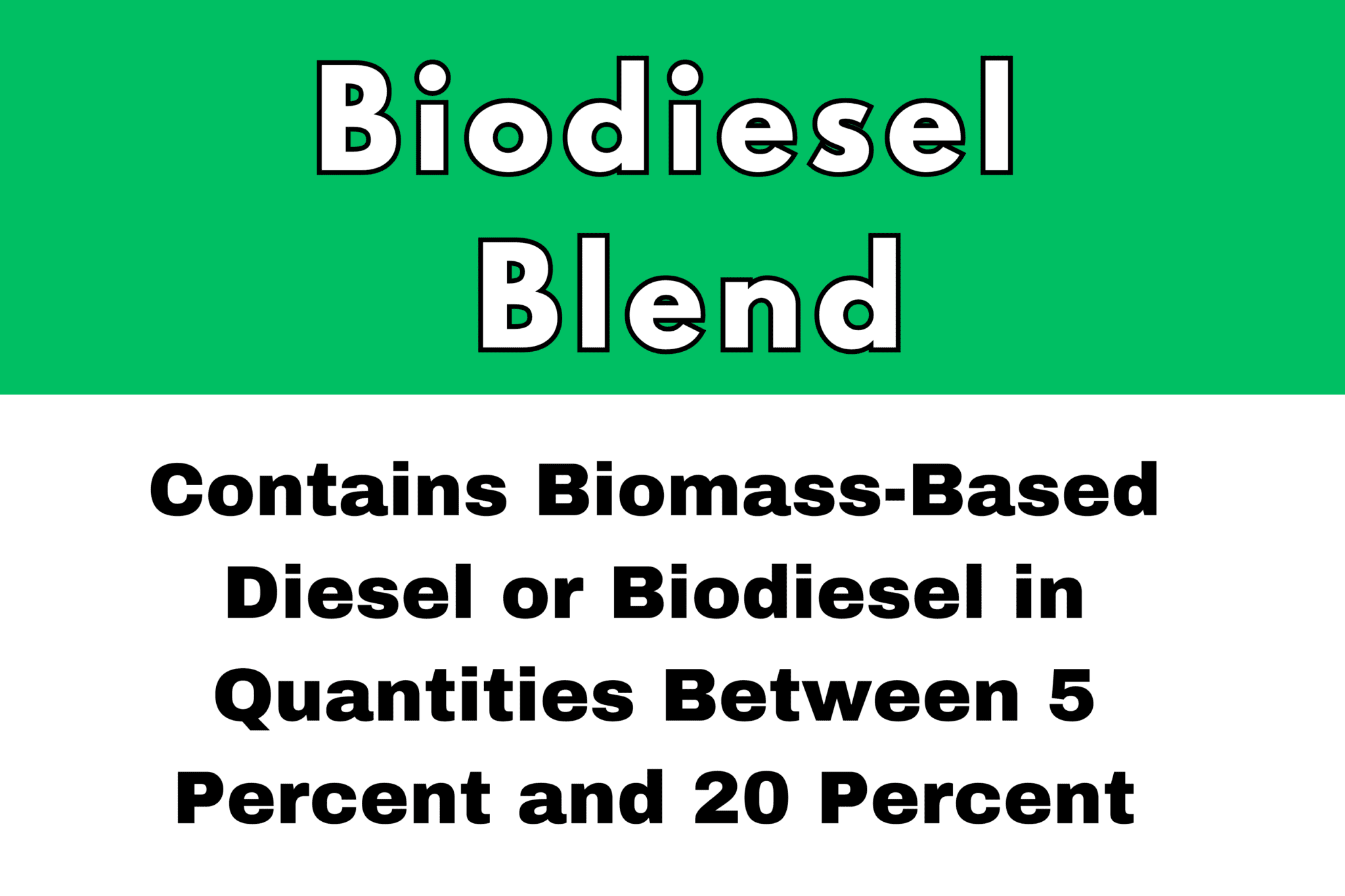
Above are a variety of labels used to denote what fuel blend is coming out of a retail diesel dispenser. Feel free to call Star Oilco at 503-283-1256 if this confuses you and you want it explained. We would be glad to do so.
These labels can be found together often at one pump. All state and Federal standards require ultra low sulfur diesel for any on-road diesel sale. The Federal standards also adopted by the states require a disclosure at the fuel pump if a blend is above 5% biodiesel. The max allowable blend of biodiesel for diesel truck manufactures is a 20% blend. If a truck dealership says that you cannot blend biodiesel up to 20% they need to take that up with the Federal Government because they need to support it. This is why the label shows a blend may contain between 5% and 20% biodiesel content.
Renewable diesel is a hydrocarbon diesel.
It is diesel meeting the ASTM D975 specification for diesel.
Retailers selling blends of R99 in their fuel do not need to label it given this. They still do label it given the benefits of the fuel’s performance and that customers are seeking that fuel.
Contact Us Today To Schedule Your Next Bulk Fuel Delivery
Many retail places will have stacked labels showing they may be blending 5% to 20% biodiesel as well as may be adding R99 Renewable Diesel to the fuel as market conditions dictate it is the more cost competitive fuel. When seeing a label like this it can usually be assumed they are blending a R80 (80% Renewable Diesel) and a B20 (20% Biodiesel) blend of fuel. This blend is actually believed by some to be a higher performing fuel seeing better performance that a R99 or B20 fossil fuel blend.
Fossil fuel diesels are being replaced or blended with biomass based diesels. Be it Renewable Diesel or Biodiesel. These blends are driven by more than one industry requirements, government rules, or other market forces. One of these being Portland’s banned on petroleum diesel through the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS). This is resulting in an increase of low-carbon biofuel blends that will ultimately move to a mix of 99% renewable fuel requirement by 2030.

The big drivers are industry specification for fuels (both labeling as well as chemical characteristics), state rules on selling these fuels, their quality assurance as well as CO2 content, and of course the market forces. Market forces being the supply and demand availability of fuel needed to meet customers. Less fuel available to sell means higher prices for customers.
A decade ago the market for diesel was far simpler. Though you had biofuels and some blend mandates basically you had a diesel specification accepted and the daily price as tracked by a lighted retailers sign, a wholesale market average or spot buying by some customers. Today this market is far more complicated by government regulation on the west coast. There are three big programs at state levels impacting this.
State Fuel Rules cause a unique need for one state or another. Whereas twenty years ago if Oregon or Washington fuel was selling for more than the Gulf Coast you might see brokers bring fuel into the region then driving down high prices. With the creation of various complex and unique rules on diesel, imports of fuel to these low CO2 fuel states has dropped. The amount of people moving product into west coast states has dropped. The big rules causing this are the Cap and Invest programs of the West Coast states, the Low CO2 Fuel Standards of the states, and the fuel blend mandates of various jurisdictions of these states. For instance California now requires all off-road diesels but 99% renewable diesel. Portland, Oregon also has a CO2 requirement and minimum 15% blend of biomass based diesel on all fuel sold in the state.
WHAT ARE THE DIESEL FUELS AND THEIR SPECIFICATIONS
Petroleum Diesel:
ASTM D975 Specification.
The ASTM D975 is a series of tests used to maintain consistent industry standard product performance for diesel fuel. It includes among several tests cloud point, cold filter plug point (CFPP), several masurements of diesel fuel operability performance, intrained water content, sediment, carbon residue, ash, distillation, viscosity, sulfur, copper corrosion, cetane number, cetane index, aromaticity, and conductivity.
Renewable Diesel:
ASTM D975 Specification.
Renewable Diesel is following the same series of tests as petroleum refined diesel fuels. It is the same ASTM D975 specification. Though Renewable Diesel has some different properties that exceed the ASTM specification of diesel. Renewable Diesel is highly prized as a fuel because it typically is a cleaner and drier diesel fuel than petroleum diesel. This being seen by the tests on sediment and water content in a parts per million level. Renewable Diesel content in diesel fuel can also be tested for looking for a C14 molecule (the chain typically created in a Hydrotreated Diesel process from fats, oils and greases.
Biodiesel (Methyl Esther):
ASTM D6751 Specification.
The ASTM for Biodiesel tests a mono-alkyl esters of long chain fatty acids derived from vegetable oils and animal fats. The testing for quality assurance covers an analysis for flash point, methanol, water and sediment, kinematic viscosity, sulfated ash, oxidation stability, sulfur, copper strip corrosion, cetane number, cloud point, acid number, carbon residue, total and free glycerin, phosphorus, reduce pressure distillation temperature, atmospheric equivalent temperature, combined calcium and magnesium, and combined sodium and magnesium.
For more on Biodiesel Use and Handling the National Renewable Energy Laboratory has a great book on the subject.
THE HISTORY OF DIESEL FUEL SPECIFICATIONS IN THE UNITED STATES
In the 1990’s the US EPA passed rules that demanded a phase out of sulfur in diesel fuel. The presence of sulfur was very good for the fuel’s storage stability as well as fuel lubricity, but was horrible for air quality. Additionally the big smog contributor was NOx (nitrous oxide) which was one of the EPA’s reason’s for pulling sulfur out of diesel. For the EPA to get engine manufacturers to treat the NOx emissions at the tailpipe they needed all the sulfur gone (ultra low sulfur diesel) for modern diesel emission systems to be able to eliminate NOx as well as a host of other pollutants including particulates.
The story of changing diesel fuel standards in the US under the EPA is one of removing sulfur from our diesel fuel. In 1996 the fuel refiners and sellers of diesel had to move the sulfur content of the fuel sold for on-road purposes to below a 500 parts per million standard. Commonly referred to as Low Sulfur Diesel fuel. In 2006 the standard moved to a maximum of 15 parts per million of sulfur for all on road fuels.
In 2006 while the sulfur content of fuel was dropping the City of Portland released the first mandated blend of biodiesel content. This being a 5% biodiesel blend. The next year, the State of Oregon followed with its own Renewable Fuel Standard requiring this throughout the state. This began the expectation of biodiesel in most diesel fuel in the Portland, Oregon area. Washington also passed a similar policy for blending biodiesel but the enforcement and need for the fuel is less specific at Washington fuel pumps.