Every Question We Have Been Asked About Renewable Diesel
Renewable Diesel Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is renewable diesel?
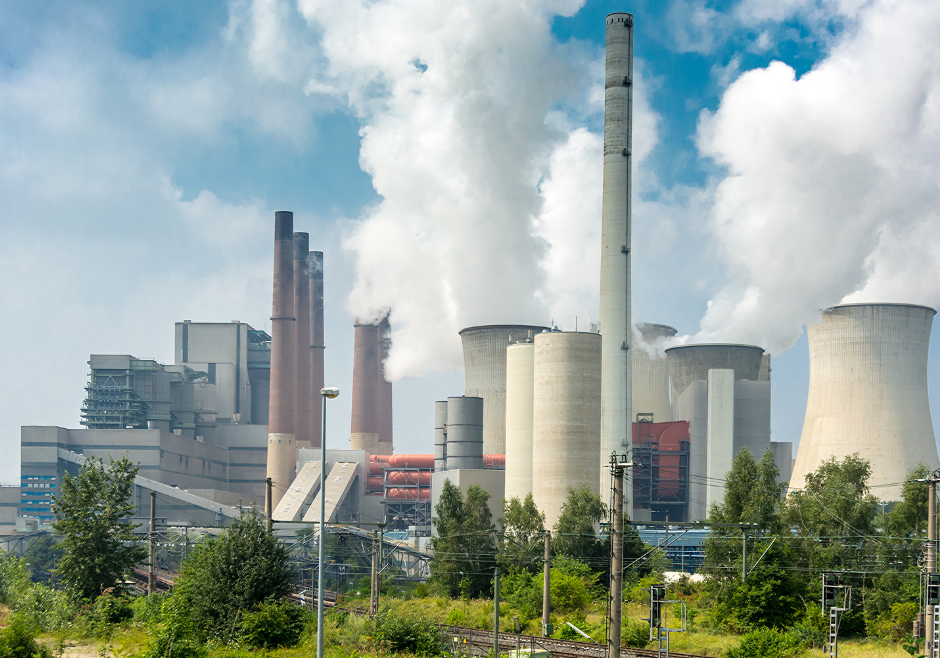
Renewable diesel is a synthetic diesel fuel, known for it’s lower CO2 characteristics, typically seeing purity and real world performance response superior to petroleum diesel fuel. Renewable diesel is a next generation hydrocarbon diesel biofuel made by either the Fischer-Tropsch or Hydrogenation processes.
Hydrogenated renewable diesel is made by taking fats, oils, and greases by use of a hydro-treater. The biomass based oil or fat is cracked and reformed in the presence of hydrogen and catalyst forming a hydrocarbon diesel molecule.
Fischer-Tropsch renewable diesel is used by converting any btu dense feedstock (wood waste, woody biomass, municipal garbage, coal, and an endless list of low value waste products into syngas, then converting this into a wax that is reformed into hydrocarbon diesel.
Is it true that Renewable Diesel reduces CO2 emissions by more than half?
It depends on the feedstock and processes that determine the fuel pathway. But for the most part it is safe to presume that if you use a R99 Renewable Diesel product in Oregon that it will have a lower than 50CI which would cut the CO2 emissions in half versus an equivalent gallon of gasoline used. Sometimes Renewable Diesel can be blended with fossil fuel diesel as well as biodiesel. Star Oilco currently presumes 99% renewable diesel is the fuel being used when describing Renewable Diesel and “cutting emissions in half” as a claim, backed up by the scientific data associated with the Oregon Clean Fuels Program and its pathways.
According to the Oregon Clean Fuels Program list of pathways for Renewable Diesel approved to be sold in Oregon shows the lowest CO2 value to be 16.36 CI and the highest to be 65CI. Most, nearly all, of the Renewable Diesel pathways in Oregon are below 50% reduction in CO2 emissions associated with the fuel. You can see these by reviewing the downloadable spreadsheet of “Fuel Pathways – Carbon Intensity Values” available on the left hand side of the Oregon Clean Fuels Program website under the heading “Participating Facilities” as an easy sharable link is not available.
To learn more about this please see the Oregon Department of Environmental Quality’s Clean Fuels Program page where CO2 emission pathways are disclosed for renewable fuels distributed in Oregon. The system used to measure CO2 emissions and reduction is a modified Oregon “GREET” model. GREET stands for Greenhouse gas, Regulated Emissions, and Energy Use in Technology. The GREET scientific system to review CO2 emissions was developed by the US Department of Energy and similar systems are used by California and Washington in their Low Carbon Fuel Standards as well.
Is HVO or Hydrogenated Vegetable Oil the same as Renewable Diesel?
Yes. HVO is either R100 or R99 renewable diesel. The reason you will hear the phrase HVO or Hydrogenated Vegetable Oil instaed of renewable diesel is that the regulations and various incentives for renewable diesel have restrictions. If renewable diesel is used in stationary power generation it is treated differently for the various subsidies and incentives. The regulations on fuels for vehicles and equipment differ compared to utility scale power generation. For this reason the power generation industry will refer to renewable diesel as “HVO” to denote it’s end use.
Is Sustainable Aviation Fuel or “SAF” the same as Renewable Diesel?
No. Sustainable Aviation Fuel or “SAF” is a Jet A specification or a Number 1 diesel fuel. A Number 1 diesel fuel can be mixed with Number 2 without impacting it’s specification requirements. Number 1 though cannot be mixed with Number 2 diesel weights and stay in specification. It is a lighter end than Number 2 diesel meaning it has a different specific gravity weight of the fuel. So in short SAF can be used as Renewable Diesel but has a much higher standard to meet than is required for Renewable Diesel. Therefore the products are very different based on this need for quality assurance to meet the aviation jet fuel specification.
There is a huge demand for Sustainable Aviation Fuel and many of the current Renewable Diesel plants in operation are upgrading their technology to make SAF. It is expected that in the hydrotreating processes to make renewable diesel and SAF, the Jet A fuel specification is a harder one to produce. So as the refining of SAF increases we will expect to see subgrade SAF (product made to be SAF that does not meet the standard) be moved to the Renewable Diesel market. We will not see Renewable Diesel being used in jets though.
Can Renewable Diesel be used as Heating Oil?
Yes. Renewable Diesel is a synthetic hydrocarbon diesel fuel. It can be used interchangeably with petroleum diesel products of similar grade. Heating Oil is typically number 2 diesel which is the same specification as Dyed R99 Renewable Diesel (or blends of Renewable Diesel with petroleum diesel). Star Oilco now offers R99 Heating Oil delivered in the Portland metro region area of Oregon.
Most modern oil heat appliances use a Becket Burner. For more on heating fuel compatibility with oil furnaces and oil burning appliance please see “Alternative Fuels and Becket Burners” for more information.
Why do people use renewable diesel over petroleum diesel?
Fleet managers operating R99 Renewable Diesel report a lower mechanical cost of operation using the fuel. Beyond the immediate benefit of R99 cutting CO2 emissions by half or more, fleets experience performance benefits from the fuel. The big savings are seen the the performance of Tier 4 Emission systems on modern diesel seeing far less wear of the Diesel Particulate Filter system as well as far fewer regenerations of the system. Additionally Renewable Diesel is a very clean and dry diesel fuel improving the storage stability, field operation, and general predictability of the fuel’s performance.
How do I know Renewable Diesel is being sold at a retail location?
Renewable Diesel is a hydrocarbon diesel that meets the specification for petroleum diesel known as ASTM D975 specification. This means currently R99 can be readily blended and sold with petroleum diesel without a disclosure. The US Federal Trade Commission and local state Weights and Measures have rules for retail pump labeling. Blend percentages of biomass based diesel must be labeled especially if being advertised. As R99 Renewable Diesel has a higher value and is sought out by many consumers though usually it is disclosed. The pump labeling for R99 Renewable Diesel typically looks like the below.

What is renewable diesel made of?
Renewable diesel can be made from a host of things, usually a low value waste product. The most common feedstock used currently is waste vegetable oil, wastes from animal rendering, and other biologically derived oils. Processes using bio-oils are following a Hydrogenation process to turn low value waste oils into high value diesel and jet fuel.
Chevron Renewable Energy Group and Diamond Green Diesel (Diamond Green is in a joint venture with Valero) are the largest producer of renewable diesel with their REG Ultra Clean Diesel product in the United States. Neste is the largest producer of renewable diesel internationally, with its “Neste My” product. being the two largest producers of low CO2 bio-oil derived renewable diesel fuels.
Major petroleum refiners have also turned around existing petroleum refineries into Renewable Diesel Refineries to produce this in demand low CO2 fuel. HF Sinclair , Marathon, Phillips 66, and Montana Renewables. There are quite a few newer Renewable Diesel projects planned and in progress around the United States as well as in the Pacific Northwest.
Other refiners of renewable diesel (on a much smaller scale of production) are using a Fischer-Tropsch process with wood waste, sorted higher grade municipal garbage, and other high btu value carbon based waste products. Many expect this to technology to be the future of all diesel and jet fuel refining turning refuse into fungible low carbon fuel.
What is renewable hydrocarbon diesel?
Renewable hydrocarbon diesel is a synthetic diesel fuel made from non-petroleum feedstocks like vegetable oil, animal fats, municipal waste, agricultural biomass, and woody biomass. It is characterized by having a low CO2 and renewable resource for its feedstock and is made without crude petroleum, coal, or natural gas as a direct feedstock input in the refining process.
How do they make renewable diesel?
Renewable diesel is made by several processes. If you are buying renewable diesel, it is probably from a Hydrogenation process used by Renewable Energy Group and Neste for their products. Other smaller volume producers are using a Fischer-Tropsch process or Fast Pyrolysis. Both processes involve taking energy dense molecules, cracking those molecules under heat and pressure, then reforming them in the presence of a catalyst and added hydrogen, which forms a renewable diesel molecule.
Is renewable diesel a lower carbon fuel compared to petroleum diesel?
Yes, to this point all renewable diesel made from renewable feedstocks have appeared to be a lower CO2 fuel compared to petroleum diesels. The California Air Research Board in particular has done research on this in depth.
The low CO2 lifecycle emissions of Renewable Diesel also is tracked closely and supervised by California’s Low Carbon Fuel Standard, Washington’s Low Carbon Fuel Standard, and Oregon’s Clean Fuels Program. The highest value markets for low CO2 fuels in the United States are California and Oregon, which both have mechanisms that track and price the CO2 intensity of diesel fuels as well as the sustainable lower CO2 substitutes and blend-stocks that can go in those diesels. They track, rate, and determine the carbon intensity of the fuels providing a neutral and scientifically defensible number for CO2 reduction.
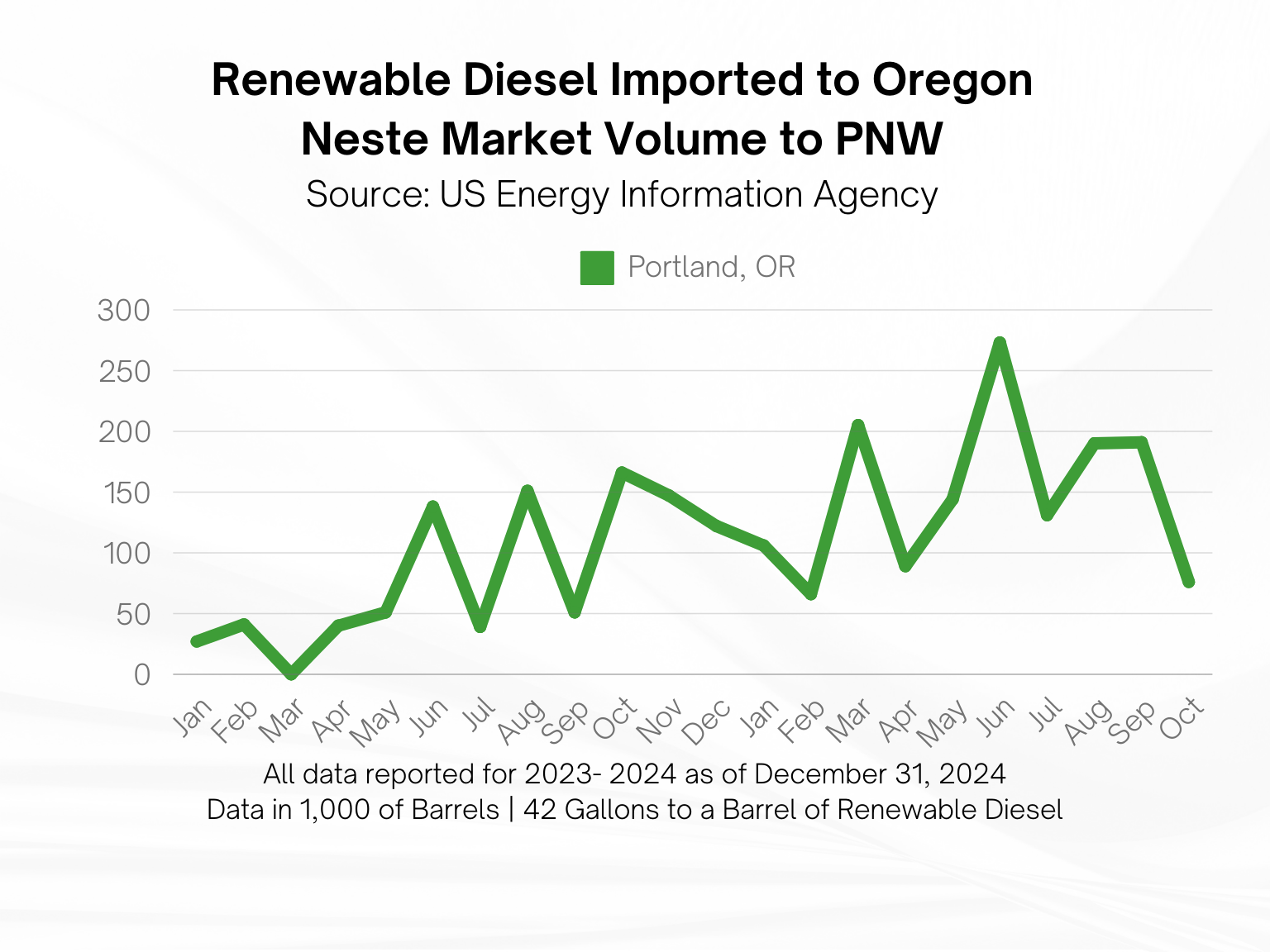
Is renewable diesel available in Oregon?
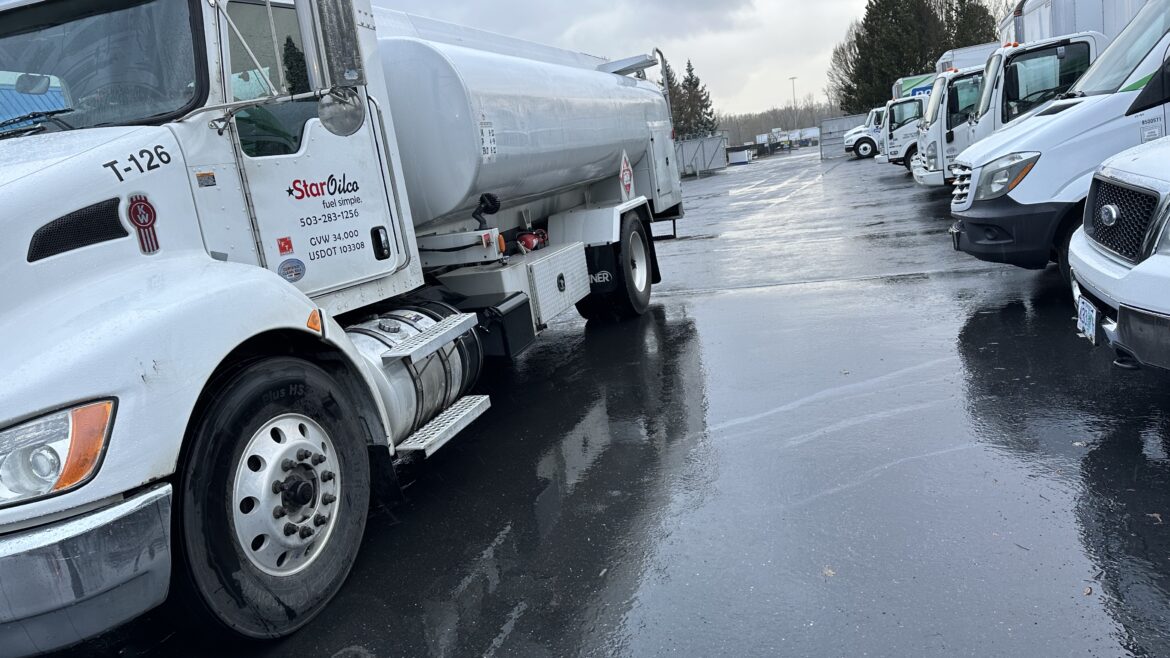
Renewable diesel is readily available for delivery from Star Oilco throughout the Pacific Northwest via 10,000 gallon volumes of bulk delivery. Star Oilco is also offering bulk delivery of any size and mobile onsite fueling service within 100 miles of the Portland, Oregon market.
Star Oilco has R99 Renewable Diesel available with a Star Oilco CFN Cardlock card in Portland, Oregon.
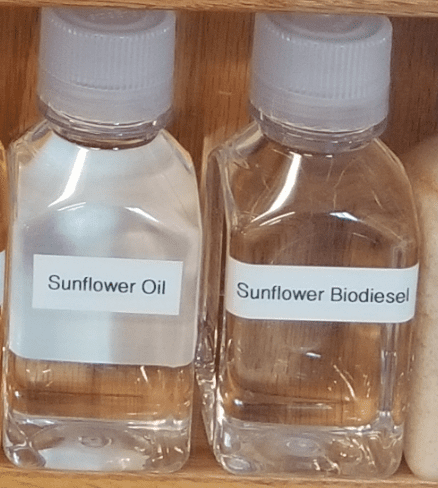
What is the difference between biodiesel and renewable diesel?
Biodiesel and renewable diesel are very different fuels made with very different processes. In a nutshell, biodiesel is made with a simple chemical reaction that turns vegetable and animal fats into fuel. Renewable diesel is made from far more complicated process where vegetable and animal fats (as well as other feedstocks) are cracked on a molecular level and built back into synthetic diesel fuel.
What is the difference between renewable diesel and Sustainable Aviation Fuel?
The difference between the fuels is the specific gravity and general specification for what the fuel is used for. Jet fuel, or Sustainable Aviation Fuel, and on-road diesel fuel are different fuels and therefore have different specifications. Renewable diesel is typically referring to a #2 diesel specification for on road diesel use.
Sustainable Aviation Fuel or “SAF” is typically referring to “Jet A” or “JP8” jet fuel specification for fuel. This is a #1 diesel range fuel with use and handling requirements that are far more stringent than for on-road or off-road diesel fuels. Renewable jet fuel can be used as a kerosene or #1 diesel fuel but renewable diesel cannot be used as a jet fuel.

Where do I buy renewable diesel in Oregon or Washington?
Renewable Diesel is currently available for bulk delivery and mobile onsite fueling. It will soon be offered at commercial cardlock in the Portland area. It is being sold as R99 and as Ultra Clean Diesel, which is a mixture of biodiesel, renewable diesel, and petroleum diesel.
What is R99?
R99 stands for 99% renewable diesel and 1% petroleum diesel. Federal rules over alternative diesel fuels made fuels requires that manufacturers of non-petroleum derived diesel fuels must blend a minimum 1% petroleum with the fuel to generate a Renewable Industry Number or “RIN” under the US Federal Renewable Fuel Standard. Additionally there are other incentives that require a “blender of record” to receive these tax credits.
Is renewable diesel being made in Oregon?
As of Spring 2022, renewable diesel is not being manufactured in Oregon. There is a major projects underway, Next Renewable Fuels in Port Westward, Oregon.
What is renewable diesel made from?
Renewable diesel can be made from many energy dense carbon based material. By volume of produced product sold in the United States, vegetable oils and animal fat-based wastes are the most common feedstock. Woody biomass, agricultural wastes, and sorted municipal wastes are also sources for renewable diesel production.
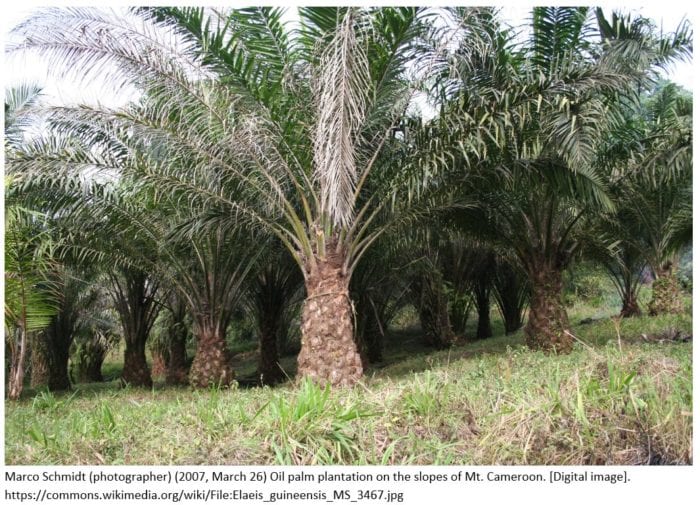
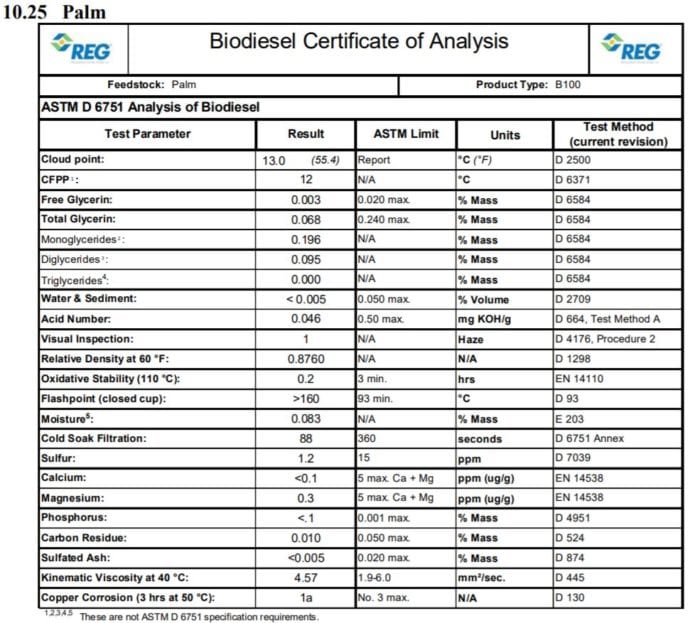
Is renewable diesel made from palm oil?
Palm oil can be used as a feedstock for renewable diesel. There are producers who use palm oil as a feedstock. In the United States, feedstocks and carbon intensity are tracked closely under both Oregon and California’s fuel programs. You can determine if a supplier is using palm oil as a feedstock through these regulated pathways.
How much does renewable diesel cost?
This is a tough question to answer given there are several markets intersecting. From the feedstocks to the market demand for the finished product as well as both California and Oregon’s Clean Fuel Standards which place a price on the CO2 intensity of the fuel which reduces the cost of the fuel if consumed in Oregon and California.
It has consistently been trending between the same cost and over $1 a gallon higher than petroleum diesel depending on the state, you buy renewable diesel in. In California, renewable diesel is very close to petroleum diesel depending on the value of CO2 credits for lower-carbon fuels. In Oregon, it has consistently been between $.05 to $.80 a gallon higher than diesel also depending on the value of CO2 abatement associated with the fuel and what these carbon credits are trading for.
When petroleum diesel costs are high Renewable Diesel tends to be more competitive with petroleum diesel. When petroleum diesel is below $3 a gallon the cost of Renewable Diesel by comparison is usually higher unless CO2 credits are in higher than normal demand for Clean Fuels Program demands.
Can you mix petroleum diesel and renewable diesel?
Yes. Renewable diesel and petroleum diesel can be blended in any mixture without worry. They are drop-in substitutes for each other in your fleet’s use. Renewable Diesel is a drop-in fuel. It is a hydrocarbon diesel that will work mixed with diesel or biodiesel blends of petroleum diesel.
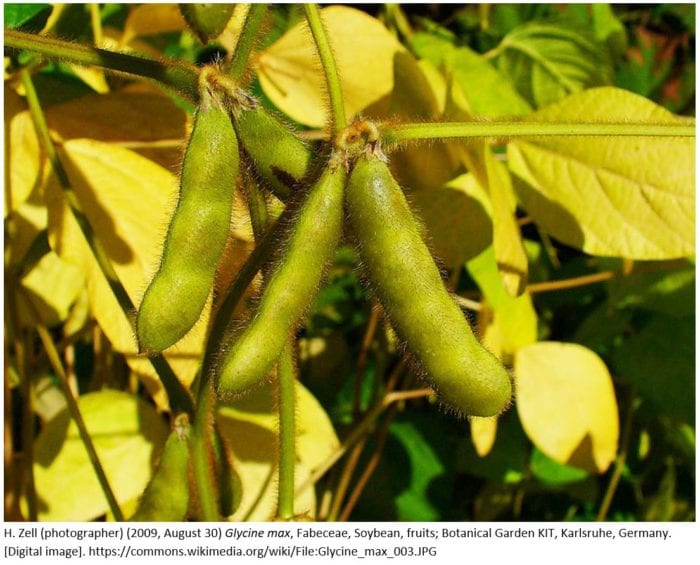
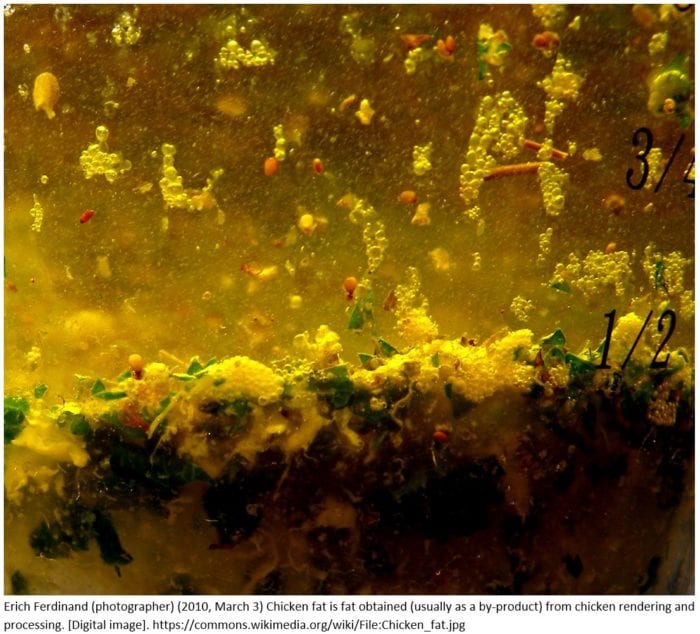
















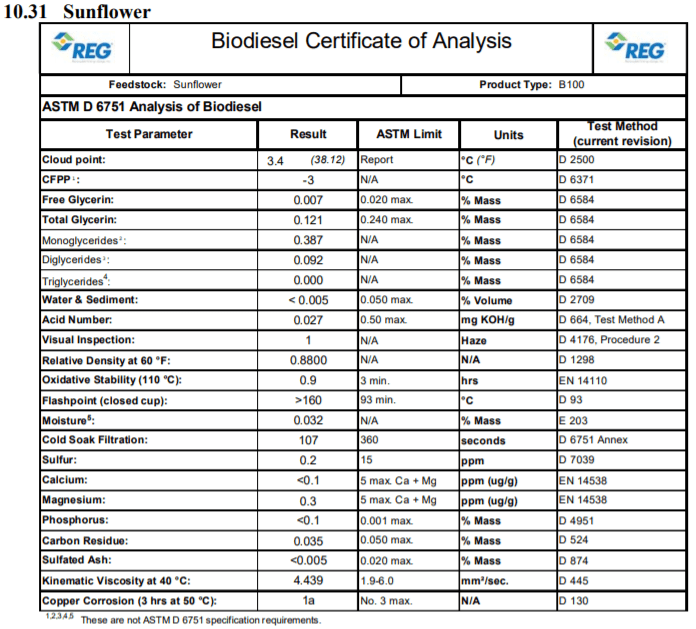


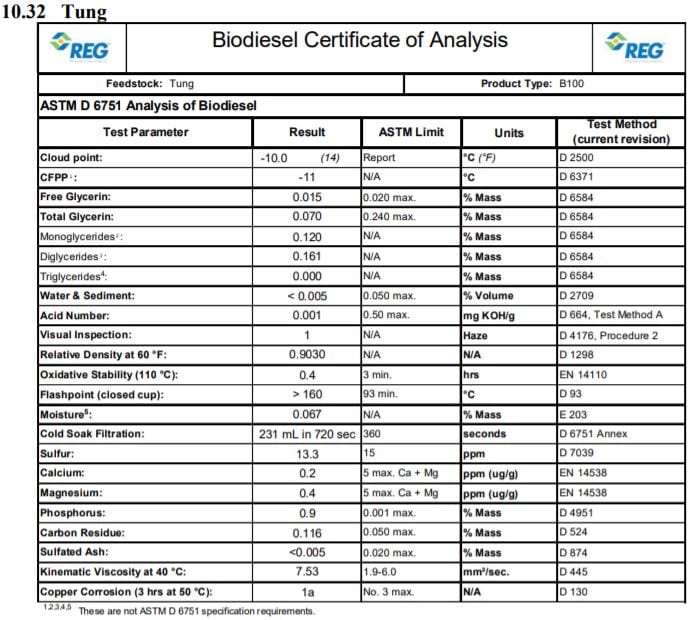



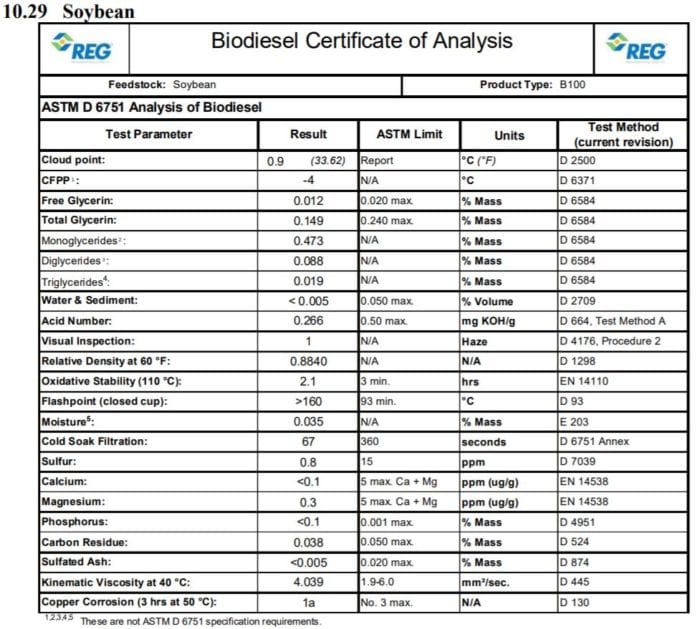
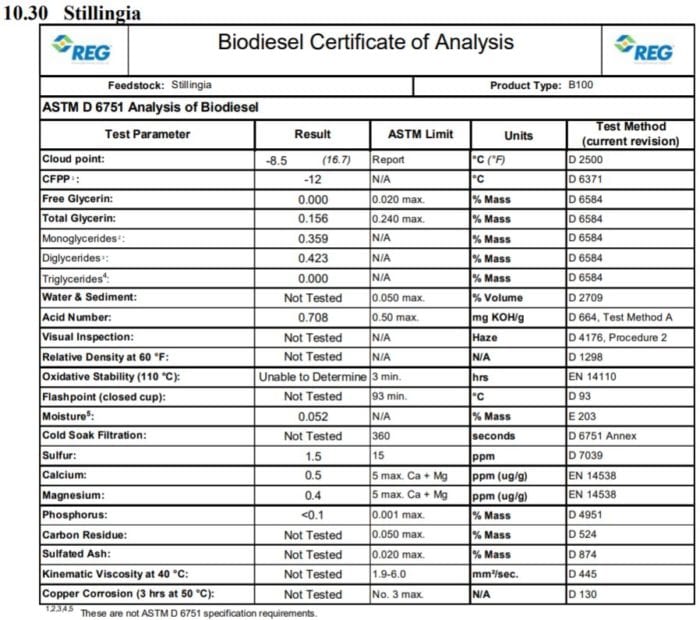
 is different from other forms of fat and tallow. It tends to have less saturated fat. According to
is different from other forms of fat and tallow. It tends to have less saturated fat. According to 
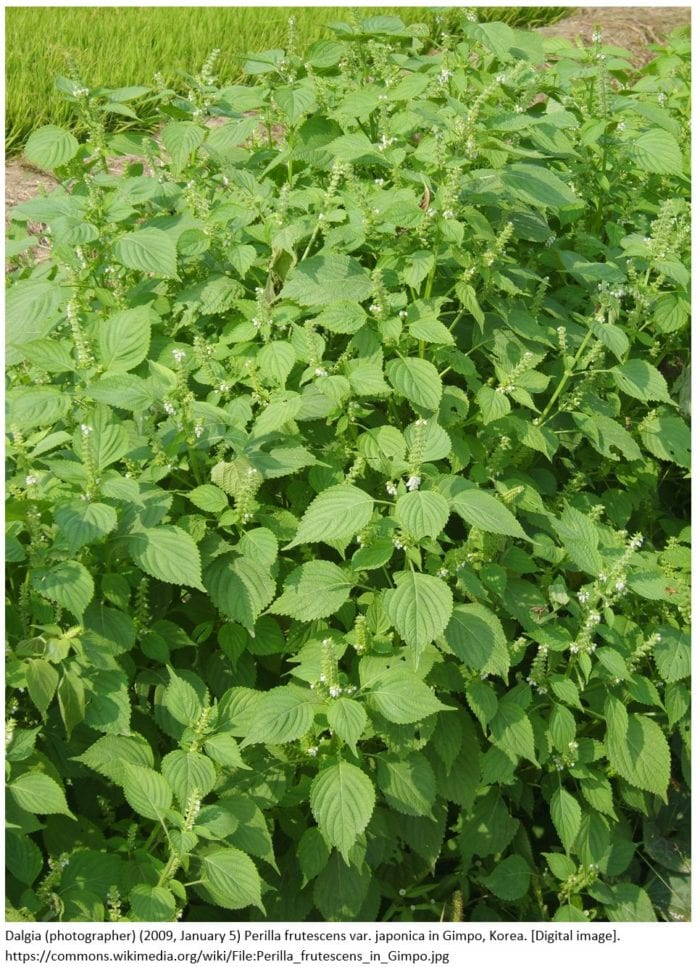



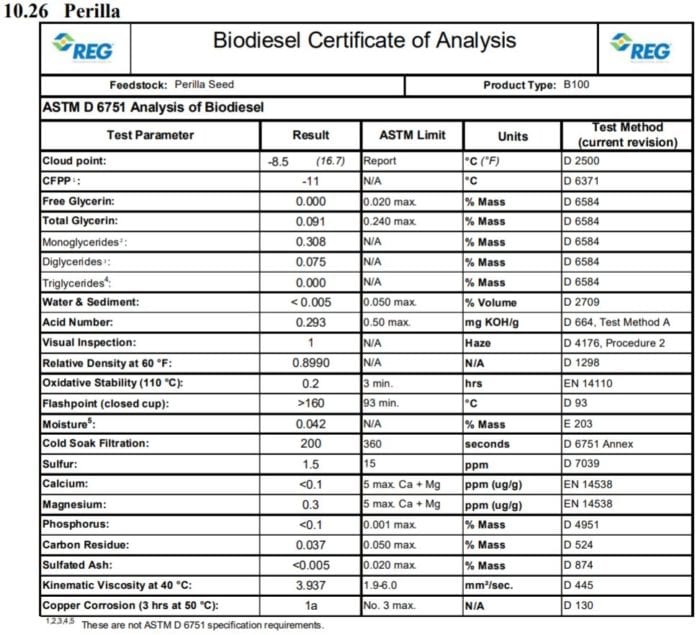
 It is native to India and China in the mountainous regions and cultivated in China, Korea, Japan, and India. Introduced varieties of this plant are considered a weed in the United States and go by the common names Chinese basil, wild basil, perilla mint, beefsteak plant, purple perilla, wild coleus, blueweed, Joseph’s coat, and rattlesnake weed. This herb grows easily unattended, but is toxic for cattle and horses.
It is native to India and China in the mountainous regions and cultivated in China, Korea, Japan, and India. Introduced varieties of this plant are considered a weed in the United States and go by the common names Chinese basil, wild basil, perilla mint, beefsteak plant, purple perilla, wild coleus, blueweed, Joseph’s coat, and rattlesnake weed. This herb grows easily unattended, but is toxic for cattle and horses.